|
 |
 |
The article goes on to point out that obesity is learnt not genetic in nearly all instance. The article compares a genetically identical group for which there were recent changes
in financial and cultural circumstances. The Pima Indians who in Arizona have
a high prevalence of obesity while just across the boarder their relatives are typically leant. Undoubtedly there are genetic factors, however, as with the Pima Indians, cultural pressures have been
shown to control this disposition to being revolting.**
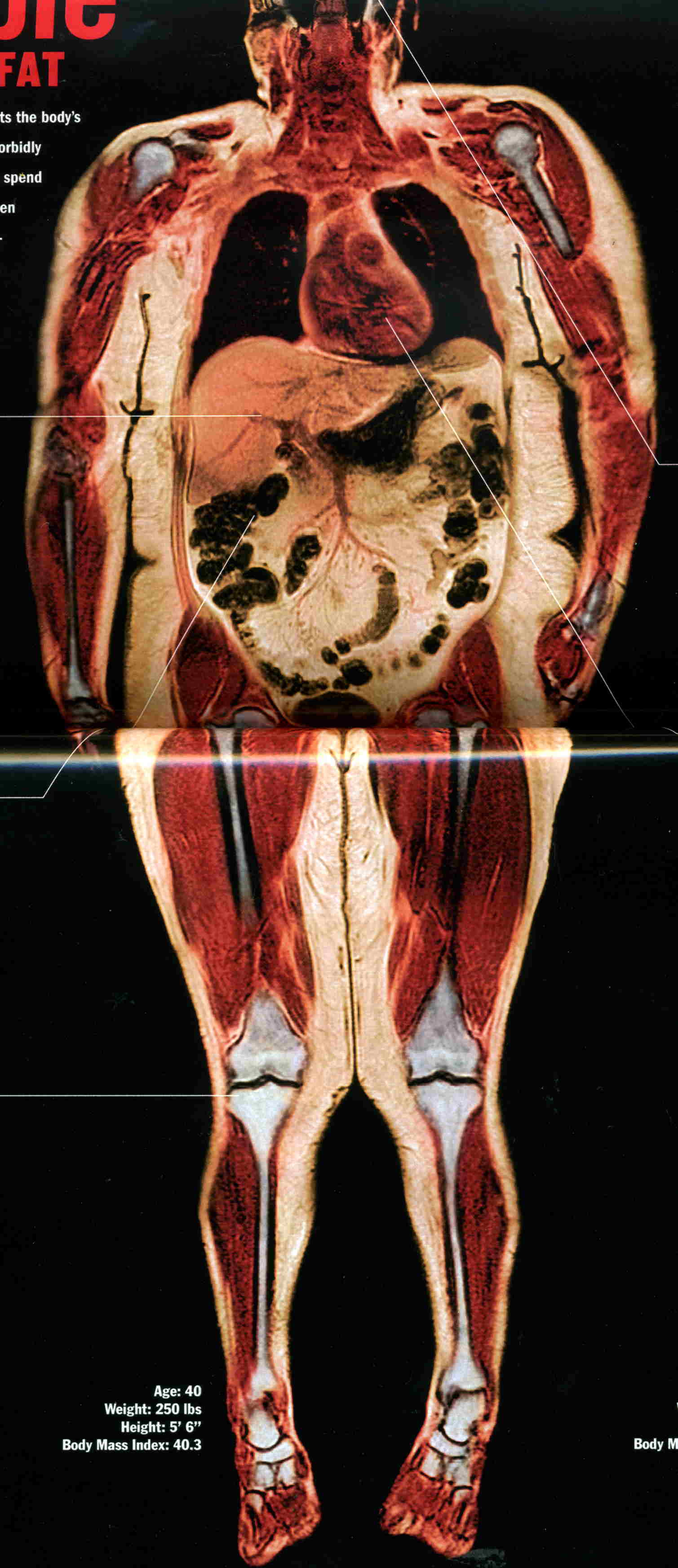
* BMI (Body Mass Index) is computed by taking the weight
in kilos and dividing by the height in meters squared (B/M2). There
are 2.2 lbs per kilo, and 39.37 inches per meter. For 6 feet and 160 lbs the BMI is 22.0, for170 lbs, BMI 23.2, and for 250 BMI 34.3.
For 5feet 6 inches 120 lbs, BMI 19.4, and for 130 lbs the BMI is 21.0; for 180 lbs the BMI is 29.1. It should be noted that women, who because of less muscles when lean weigh less than a man of the same
height who is equally lean, that such woman on an average are longer lived. Thus
the higher BMI for the lean man than a lean woman is consistent with the longevity of woman.
** Though not made in the article, I should point
out that any trait which is disadvantages, either to survival or reproduction, will become rare. This has been proven by numerous population studies. Obese
people reproduce less; therefore, any and all genetic causes would become rare. Thus like smoking obesitys primary causes
must be social.
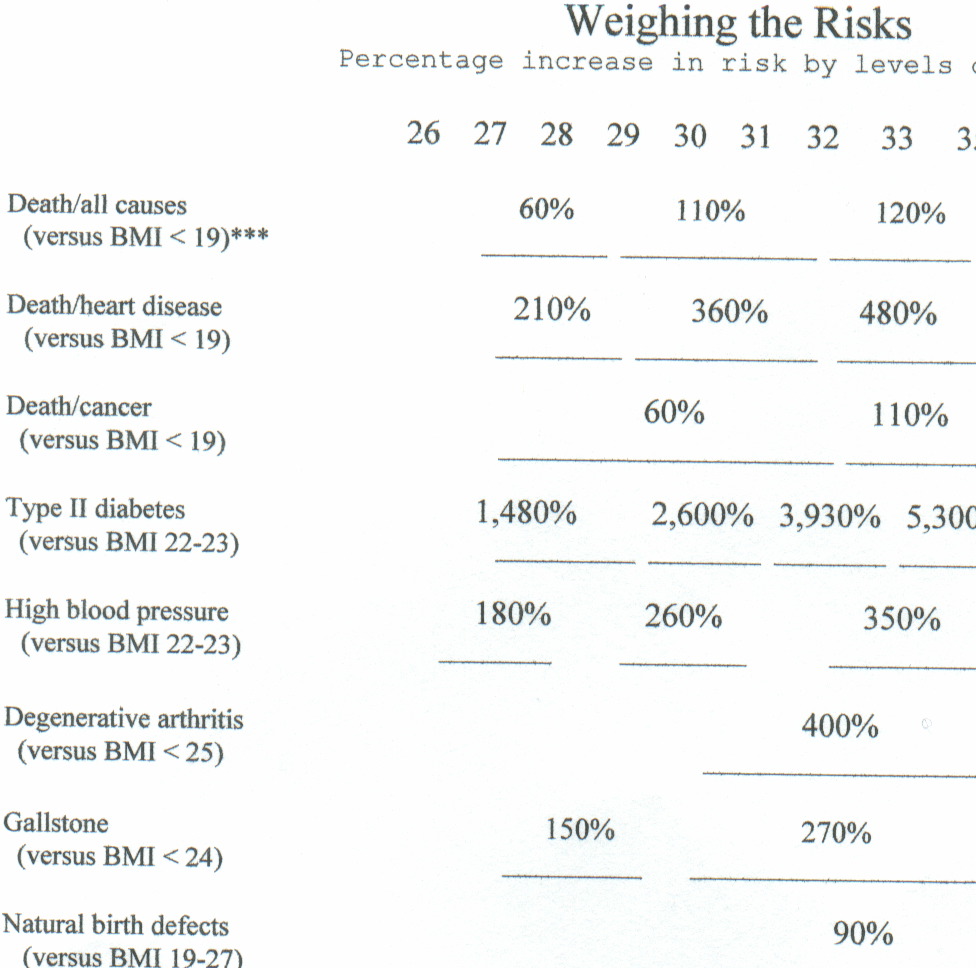
A recent study found a very
strong connection between alzheimer's disease and obesity. For
those over 50% above their lean body mass the increase risk was over 150%.
U.S. Is Still a Nation of Excess
Childhood Obesity, Adult
Obesity Are Still Big Problems
June 15, 2004 -- A new study provides a snapshot of the nation's obesity problem --
and it's not a pretty picture. More than half of adults are still overweight or obese, and one-third of children is at risk
for overweight or is overweight.
From 1999 to 2002, the number of overweight Americans continued to increase, according
to the nationwide survey from the CDC. It is published in this week's Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
"There is no indication that ... obesity among adults and overweight among children
is decreasing," writes researcher Allison A. Hedley, PhD, with the CDC. "The high levels ... remain a major public health
concern."
Between 1999-2000 and 2001-2002:
- Americans were still overweight or obese -- 66% -- compared with 65% in 1999-2000.
- The number of obese Americans was also unchanged -- 31%.
- The number of extremely obese Americans was also unchanged -- 5%.
From 1999 to 2002:
- More than 50% of adults were overweight or obese; this was true in almost every
age and racial/ethnic group.
- 28% of men over age 20 were obese across all racial and ethnic groups.
- 33% of women over age 20 were obese -- but with significant differences among
racial and ethnic groups.
- 49% of all black women were obese, compared with 38% of Mexican-American and
31% of white women.
- 14% of black women were extremely obese -- the highest number of any ethnic/racial
group, whether male or female.
Among children:
- 30% were overweight or at risk for being overweight in 1999-2000 versus 32%
in 2001-2002.
- 15% were overweight in 1999-2000; 17% were in 2001-2002.
- Black and Mexican-American children were at a significantly greater risk of
becoming overweight, compared with white children.
There is no indication that obesity in adults and children
is decreasing, Hedley concludes.
This articles ties the pieces together. High levels of blood glucose has been know of decades to be associated with aging and coronary disease. This article describe the varied effects of the failure to regulate the level of glucose
due to insulin resistance. Obesity is the most significant cause of insulin resistance.
THE
INSULIN CONNECTION
U.S. NEWS.COM
By Brenda Goodman Mon Aug 29, 5:33 PM ET
Diabetes drugs have made a big difference to George Marincin and Kristin Chapman.
For a few weeks last year, Marincin, 77, from Tacoma, Wash., took artificial insulin, the hormone that's deficient in diabetics.
And every day Chapman downs doses of Glucophage, a drug that helps the 38-year-old from Atlanta to better control the hormone.
But neither Marincin nor Chapman has diabetes.
What Marincin does have is Alzheimer's disease. He took insulin to test the idea that low levels might be linked to memory problems. "I did wonder how insulin could
help George because he's not diabetic," says his wife, Mabel. "But it has. It's wonderful." Her husband has regained his sense
of humor and can even complete simple tasks again like making a cup of tea, she says. Last month his doctors reported in the
Archives of Neurology that other patients also seemed to benefit.
Chapman was just as surprised that adjusting insulin levels could help her. She has
polycystic ovary syndrome, which causes infertility and dramatically raises her risk for heart disease. But her problem wasn't
too little insulin but too much, which prevents ovulation. After seven years of struggling to conceive, she started taking
Glucophage and was pregnant in a month. "It's mind boggling, isn't it?" she says. Now the happy mother of two kids, she'll
stay on the drug for the rest of her life to keep her high insulin in check.
Insulin problems--too much or too little--go far, far beyond diabetes. The condition
is called insulin resistance and, in addition to the ailments dogging Chapman and Marincin, doctors are now discovering it
is linked to heart attacks, strokes, and several kinds of cancer and may affect 1 in 3 American adults. These findings have
alarmed many specialists. "Insulin resistance is very common, and it's associated with the biggest killers," says endocrinologist
Ronald Kahn, director of the Joslin Diabetes Center at Harvard University. "If we don't start paying attention to this now,
we're all going to be paying a huge price for this condition." Physician David Katz, director of the Prevention Research Center
at Yale Medical School, adds that "we're just beginning to understand that insulin throws a lot of big switches in the body.
Is insulin the master control of all disease? I don't know, but it's certainly a candidate for that role."
Insulin's main job is to escort sugar out of the blood and into muscle and fat cells.
But sometimes those cells resist letting it in. So the pancreas, which makes insulin, tries to crank out even more. If it
can't, blood sugar climbs to dangerous levels and the result is Type II diabetes. More often, however, the pancreas does
make more insulin. The extra hormone may restore blood sugar to normal, but it overwhelms the rest of the body. That spells
trouble, because insulin is more than just a sugar ferry. It tells the kidneys, for example, to hold on to salt. And more
salt means hypertension. It tells cancer cells to grow, and that can mean a tumor.
Fortunately, doctors are starting to devise new ways to treat insulin resistance--which
is sometimes called "metabolic syndrome" --with drugs and lifestyle changes. They are still working out all the connections,
but already they have a list of some of the leading insulin-related illnesses:
Cancer
Insulin stimulates cell growth, and unfortunately cancer cells have six to 10 times
the number of insulin receptors--molecules that grab on to the hormone--as do normal cells. So if extra hormone hits a pre-existing
cancer cell, it makes a bad thing much, much worse. "For cancer, insulin is like pouring gasoline on a fire," says Edward
Giovannucci, who studies the epidemiology of colon cancer at the Harvard School of Public Health.
Colon, breast, endometrial, pancreatic, and prostate cancers seem especially responsive.
"We think breast cancer cells may have very special kinds of receptors, fetal insulin receptors, that are ultrasensitive to
insulin," says Pamela Goodwin, director of the Marvelle Koffler Breast Center at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto. Insulin
may also influence estrogen, another hormone that can trigger tumor growth. "So if you turn on one hormone, you turn on the
other," Goodwin says. She is currently testing Glucophage to see if it can lower insulin levels in breast cancer survivors
and plans to see if this affects cancer recurrence.
Cardiovascular Disease
High levels of insulin in the blood damage the lining of arteries, increase bad blood fats such as triglycerides and
LDL cholesterol, and clump blood cells together so they are more likely to block up vessels. These observations prompted Gerald
Reaven, the Stanford endocrinologist who first described insulin resistance in the 1980s, to finger the condition for heart
attacks, strokes, and cases of high blood pressure. Other research has come to
back him up. A major study by Finnish researchers in the journal Circulation followed almost 1,000 men for 22 years
and found insulin levels alone were the most powerful predictors of heart attack risk, especially in younger men. They were
more powerful than obesity levels and physical inactivity, for example. Men with the highest insulin levels had more than
three times the heart attack risk of those with the lowest. [Obese people are much more likely to have high insulin levels—jk]
The concept does have its critics. Last week in the journal Diabetes Care , Richard Kahn, chief scientific and
medical officer for the American Diabetes Association, wrote an article questioning whether the idea of insulin resistance
is truly useful, particularly when it comes to diagnosing and helping heart patients. Just calling something by a new name,
he argues, doesn't change the recommended therapies. "I don't see the value . . . especially when the treatments are the same,"
says Kahn. He points out that if patients have high cholesterol, they're going to get cholesterol-lowering drugs and advice
on diet and exercise, whether or not insulin resistance is the root cause.
But other experts see value in understanding insulin's role in the clustering of cardiovascular risk factors, particularly
if it points the way toward new treatments. It's already doing that for stroke, for it's here that one new treatment is being
tested. This spring the
National Institutes of Health began a study at more than 60 research sites to see if the drug Actos, an insulin sensitizer, can reduce stroke recurrence
in certain patients.
Ovary Disease
According to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, polycystic ovary
syndrome affects 1 in 10 women and is the leading cause of infertility in the United States. High levels of insulin trigger
excess production of other hormones by the ovaries, disrupting regular egg growth and menstrual cycles and preventing pregnancy.
Some of these overproduced hormones, or androgens, can also cause male-pattern hair growth on the face and some other unpleasant
appearance changes. Basically, says Mark Perloe, an Atlanta endocrinologist and polycystic ovary syndrome specialist, "insulin
is driving the ovary crazy."
Doctors now treat this ovary syndrome with insulin-sensitizing medications like those
taken by Chapman, and also recommend weight loss, which lowers insulin levels. Treatment is important even beyond fertility
problems, because untreated women with the polycystic syndrome have more than seven times the risk of heart disease and three
times the risk of diabetes of women without it.
Alzheimer's
Cells in the brain's memory and learning centers have a lot of insulin receptors.
A quick spike in insulin improves memory and performance; take insulin away, and brain function begins to decline. But paradoxically,
more insulin in the blood--insulin resistance--means less in the brain. One leading theory: Insulin's corrosive effects on
blood vessel linings gums up tiny portals in the vessels that supply the brain, making it harder for the hormone to bring
in sugar. Ultimately, this starves brain cells, suggests researcher Suzanne Craft of Veterans Administration Puget Sound Health
Care System. That could set the stage for some cases of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases. Insulin also
seems to clear away some beta-amyloid, a substance long implicated in Alzheimer's damage, so less of it could cause problems.
There are, of course, many theories about Alzheimer's, and this is far from the final
word. But whatever the reason for the disease, there is preliminary evidence that getting insulin to the brains of Alzheimer's
patients improves symptoms. In Craft's recent study, a small group of Alzheimer's patients, including Marincin, inhaled insulin.
(Inhalation provides more of the hormone to the brain.) Compared with a group that only inhaled saline solution, these patients
better recalled stories and lists. It's not known, however, how long these improvements last. Craft is now testing the insulin
sensitizer Avandia in people with Alzheimer's to see if it might slow down the disease.
The tests of all these drugs may sound good, but they are far from the only treatment--or
the best--for insulin resistance. There's a lot of hope to be found around the dinner table. Most people with resistance
can actually undo it by losing as little as 5 to 20 pounds. The best eating plans, say experts, offer lots of soluble
fiber, the kind found in berries and beans and whole oats, which seems to indirectly diminish resistance, as well as lean
proteins like fish. Saturated fats may cause insulin to spike, so look for foods with healthy fats like nuts and avocados.
But enjoy them in moderation.
Weight loss is important because all the risks for all the diseases
associated with insulin resistance are multiplied by obesity. That spare tire many of us carry around the middle
packs the liver in fat, and the liver responds by tossing high levels of free fatty acids into the blood. These fats seem
to block insulin from docking with its receptors on cells, increasing the risk of starting the resistance syndrome.
Regular exercise also helps muscles better use insulin, so in addition to her medication,
Kristin Chapman works out four times a week. She also gets her heart checked every year, and has started getting regular mammograms
early, at age 35. If insulin does indeed turn on many diseases, she plans on doing her best not to throw the switch.
SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN ARTICLE
Sept 14,2005 at http://www.sciam.com Study
Assesses Annual Cost of Obesity to Employers
Study Assesses
Annual Cost of Obesity to Employers
There are
a variety of health risks associated with obesity. The condition can be hard on the corporate wallet, too, owing to medical
expenses and missed days of work. A new study has concluded that the annual additional cost for an obese worker can reach
$2,500.
Scientists at RTI International Health, Social and Economics
Research and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used two data sets that encompass more than 45,000 full time workers
between the ages of 18 and 64 for the new analysis. They compared figures that included body mass index (BMI), sick days and
total medical expenditures. In general, a BMI greater than 25 is considered overweight. The researchers found that as BMI
increased, so too did medical expenses for both men and women. The additional costs ranged from $162 for slightly obese men
to an extra $1,524 for men with a BMI greater than 40. For overweight women, these costs ranged from $474 to $1,302. When the team factored in the cost of lost work days
for obese employees, they calculated that the per capita cost of obesity amounts to between $460 and $2,485 annually.
|
|
|
|
Taking the
frequency of obesity into account, as well as the overall gender makeup of the workforce, the authors argue that for a firm
with 1,000 employees, obesity would cost about $285,000 a year. "As the prevalence and cost of obesity in the workplace continue
to increase, so does the financial motivation to search for strategies to reduce these costs," remarks study co-author Eric
Finkelstein of RTI. "Such strategies may include work site wellness and disease-management programs related to obesity." --Sarah
Graham |
|